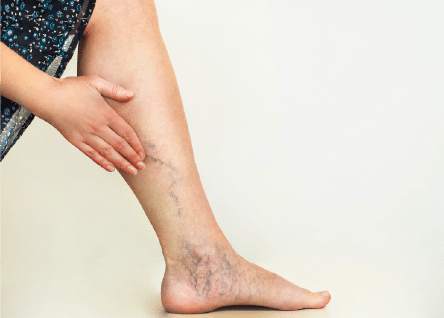
Varicose veins are a part of a group of disorders called chronic venous disease. About 23% of adults in United States are affected by this disease, if spider telengactesia and spider veins are also considered then the prevalence rises to about 80%. The disease refers to the presence of gnarled and tortuous veins generally in the leg or feet. The dilated veins can be accompanied by small, thin, red capillaries called spider veins.
Causes of Varicose Veins
This disease is caused due to multiple reasons, like weakening of the wall of the vein, incompetence of the valves between the deep and superficial vein, and venous hypertension. Weakening of the wall of the vein leads to dilation of the vein hence making the valves inside them incompetent leading to backflow of the blood from the deep veins to the superficial veins, which manifests in the form of gnarled and tortuous veins. Studies have shown there are multiple factors affecting the prevalence of this disease, these are
- Gender: Women are more likely to have varicose veins than men.
- Age: Prevalence increases with age.
- Body mass index: Higher the BMI more are the chances that the individual will have varicose veins.
- Pregnancy increases the risk of varicose veins
- Occupational and lifestyle: There is some evidence to suggest that varicose veins are more prevalent in individuals with a sedentary lifestyle and in individuals whose jobs require them to stand for prolong intervals.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
- Dilated purple, blue colored veins visible on your leg
- Feeling of heaviness and throbbing over the affected area or sometimes the whole leg
- Pain in the leg that worsens with prolonged standing
- Itching, tightness
- Discoloration of skin
- Painful cord like vein accompanied by redness
- Recurrent bruising
- Water blisters
- Slowly healing ulcers, this is a sign that the disease has progressed and you need medical attention.
- Recurrent blood clots
Diagnostic Tests
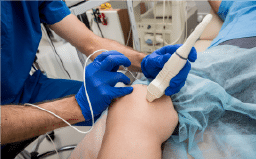
For confirmation your doctor might order an Ultrasound. During the ultrasound, the sonographer will use the probe to look for the valve competency in the affected limb to identify the location of the defect, along with thrombus, occlusion of veins.
Treatment of Varicose Veins
Depending upon the severity of the disease your doctor might suggest one or more of the following treatment plans:

Compression Stockings: for uncomplicated varicose veins the doctor might advise you to wear 20-30 mmHg compression stockings, they increase the pressure on the limb and reduce the pooling of blood. They help reduce the symptoms of the disease but there is very little evidence to suggest that they prevent the occurrence or stop the progression of the disease.
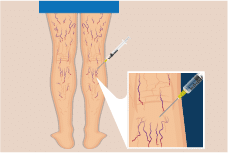
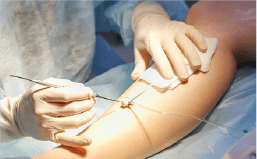
Endothermal Ablation: This is an minimally invasive procedure with high technical efficacy and rapid recovery time. For this procedure you will first be given local anesthesia, a catheter is then inserted into the affected vein and positioned near the incompetent valve. The catheter produces thermal energy which leads to destruction of the vein and permanent occlusion. According to the source of heath the procedure is called Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA).
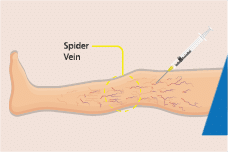
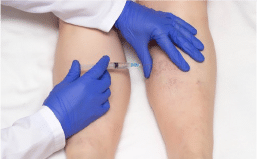
Ultrasound Guided Foam Sclerotherapy: Using ultrasound as a guide, a chemical foam is injected into the affected vein which leads to permanent occlusion, a minimally invasive technique.
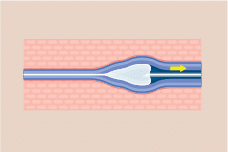
Complications of Varicose Veins
Untreated varicose veins may lead to the development of superficial thrombophlebitis, bleeding, discoloration and thickening of skin, non-healing ulcers, infection, possible limb amputation.
Prognosis of Varicose Veins
After the treatment you will be required to take some precautions to ensure that there is no recurrence; these include mild exercise, keeping legs elevated during sleeping and when you need to stand for extended period of time, to take breaks at regular interval to make sure blood doesn’t pool in your legs.
treatments we offer
The good news is varicose vein can be treated effectively.
Have our vein specialist examine your legs and recommend a treatment program that works perfectly for your specific condition.