Peak Heart & Vascular
Multispecialty Cardiovascular Group located in Laveen, Surprise, Avondale, Phoenix, and Flagstaff, AZ
Preventive cardiology is an approach to heart health that aims to reduce your risks of heart problems and identify conditions before they reach a serious stage. At Peak Heart & Vascular in Laveen, Surprise, Avondale, Flagstaff, and Phoenix, Arizona, the team of board-certified cardiologists assess your risk factors, help you make changes to minimize those risks, and provide expert treatment for a comprehensive range of cardiac conditions. We are a full service provider of diagnostic and preventive cardiology services.
Preventive Cardiology Q & A
What is preventive cardiology?
Preventive cardiology services at Peak Heart & Vascular aim to help you avoid the pain, disability, and potentially fatal consequences of heart-related health conditions.
Heart disease and many of the causes of heart problems are often lifestyle factors that you can control yourself. These include:
- Excess bodyweight
- Diet high in fat and sugar
- Chronic stress
- Being unfit
- Smoking
- High intake of alcohol
To make sure you’re optimizing your heart health, Peak Heart & Vascular can assess your risk factors and help you make the changes required to prevent heart problems.
What does preventive cardiology involve?
The preventive cardiology services at Peak Heart & Vascular involve undergoing comprehensive cardiac screening and assessment.
Screening tests that help to evaluate your heart function include:
- Blood pressure readings
- Blood glucose measurement
- Lipid level appraisal
- Noninvasive stress testing
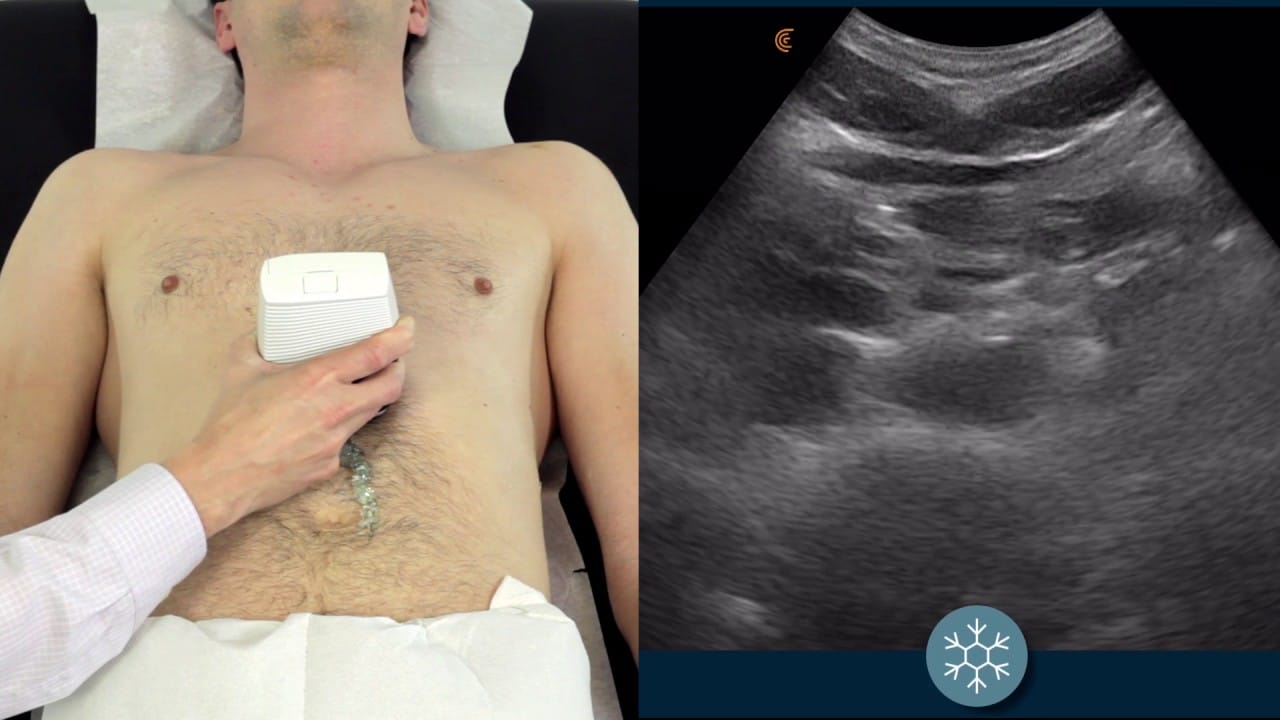
- Doppler ultrasound
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) procedures
These tests can help identify any possible problems with your heart like coronary artery disease and valvular heart disease. If there’s any sign of a problem, you might also need to undergo an ultrasound of your heart (echocardiogram). Peak Heart & Vascular performs echocardiograms on-site.
How does preventive cardiology help improve my heart health?
Most people understand that being overweight and not getting enough exercise is bad for you. However, it’s easy to put off doing anything about it unless you have some motivation.
Discovering your heart is at risk thanks to preventive cardiology can give you a real kickstart to making changes. The experienced team at Peak Heart & Vascular helps by providing you with the information and support you need to make the right choices for a heart-healthy life.
They also excel in using noninvasive therapies and minimally invasive procedures to treat heart problems before they become life-threatening. For example, conditions like high blood pressure and coronary artery disease can lead to fatal heart attacks, cardiac arrest, and stroke, but respond well to early intervention.
Preventive cardiology isn’t just useful for stopping heart problems from getting any worse. It can also play a crucial role in reducing your risk of ever developing heart disease.
For the most effective protection of your heart from present and future problems, contact Peak Heart & Vascular. Call their office today or book an appointment online.