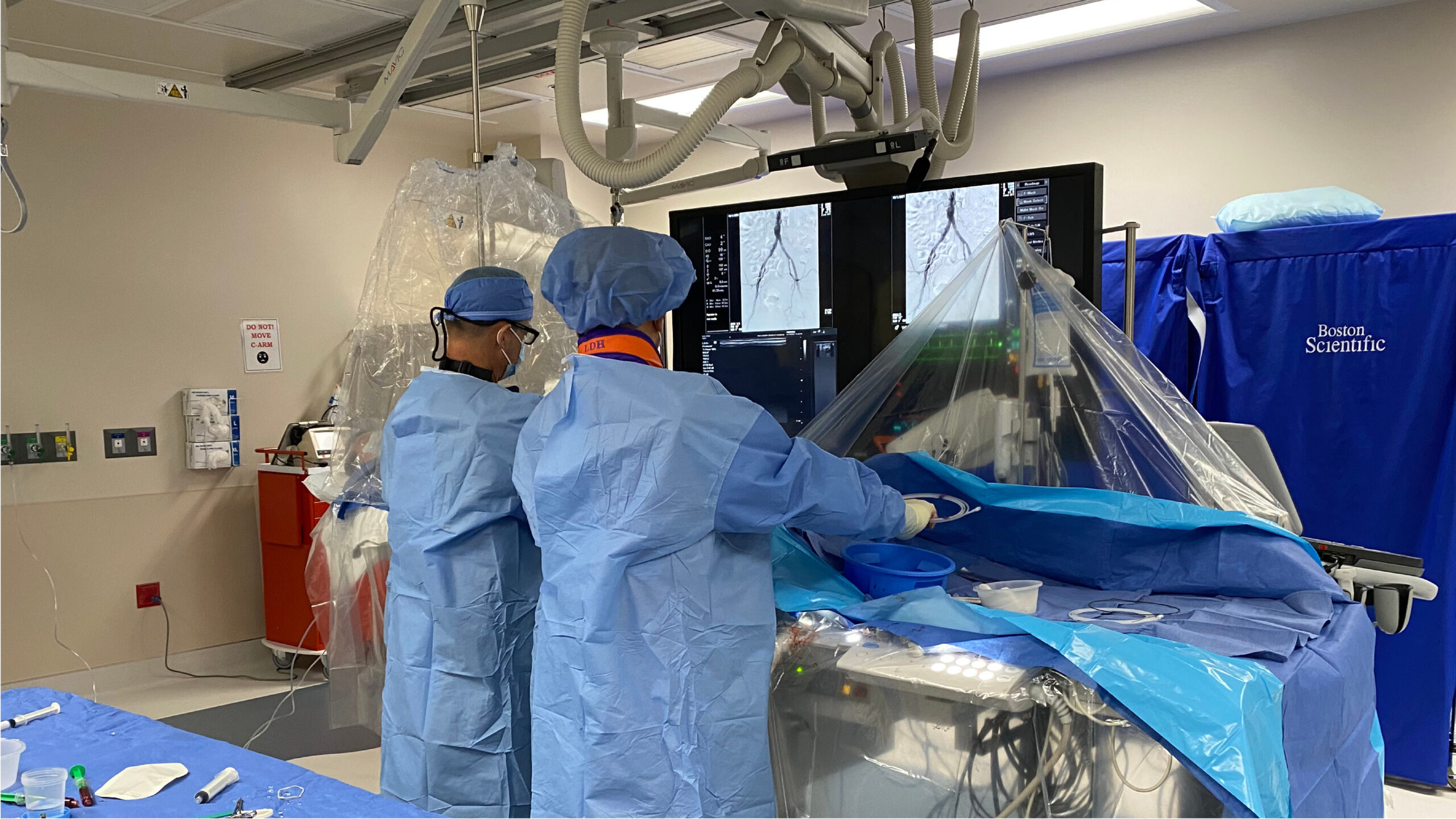
Interventional cardiology is a specialized branch of cardiology that focuses on using minimally invasive, catheter-based techniques to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. Interventional cardiologists are highly trained in procedures that allow them to treat heart and vascular diseases without the need for open surgery. These procedures typically involve inserting a catheter through a small incision, usually in the wrist or groin, to reach the heart or blood vessels. The goal is to restore normal blood flow, improve heart function, and prevent future complications.
Common Conditions Treated
Interventional cardiologists treat a wide range of heart and vascular conditions, including:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Narrowing or blockages in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart, often leading to chest pain (angina) or heart attacks.
- Heart Valve Disorders: Conditions like aortic stenosis or mitral regurgitation, where heart valves don’t function properly.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Narrowing of arteries in the legs or arms that reduces blood flow and can lead to pain, ulcers, or even limb loss.
- Atherosclerosis: A build-up of plaque in the arteries that can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Heart Attacks (Myocardial Infarctions): Blockages in the coronary arteries that cause damage to the heart muscle.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Structural heart issues that are present from birth, which can sometimes be corrected with catheter-based techniques.
- Chronic Total Occlusions (CTO): Complete blockages in the coronary arteries that persist over time, causing reduced heart function.
Common Treatments and Procedures Performed
Interventional cardiologists perform a variety of minimally invasive procedures to treat cardiovascular diseases. Some of the most common treatments include:
- Angioplasty and Stenting: A procedure where a balloon is inserted and inflated at the site of a blocked artery to widen it, often followed by placing a stent to keep the artery open and maintain blood flow. This is commonly used to treat CAD and PAD.
- Coronary Atherectomy: A technique used to remove plaque build-up from the walls of arteries, often combined with angioplasty or stenting.
- Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR): A minimally invasive procedure to replace a narrowed aortic valve (aortic stenosis) without the need for open-heart surgery.
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Also known as coronary angioplasty, this is a non-surgical procedure to open up blocked coronary arteries to improve blood flow to the heart.
- Percutaneous Mitral Valve Repair: A minimally invasive procedure using devices like MitraClip to repair a leaking mitral valve, improving heart function without the need for open surgery.
- Balloon Valvuloplasty: A procedure to widen a narrowed heart valve by inflating a balloon inside the valve, improving blood flow and valve function.
- Carotid Artery Stenting: A procedure to treat carotid artery disease, where a stent is placed in the carotid artery to prevent strokes by restoring blood flow to the brain.
- Closure of Atrial Septal Defects (ASD) and Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO): Catheter-based techniques to close holes in the heart that may lead to complications like stroke or heart failure.
When to See an Interventional Cardiologist Surgeon
You should consider seeing an interventional cardiologist if:
- You have been diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD) and are experiencing symptoms such as chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or fatigue.
- Your doctor has identified blocked arteries, either in your heart or peripheral arteries, that require treatment to restore blood flow.
- You have been diagnosed with a heart valve disorder (such as aortic stenosis) that may require a catheter-based treatment like TAVR.
- You have experienced a heart attack and need emergency intervention to open blocked coronary arteries.
- You have congenital heart defects or structural heart issues that could benefit from interventional procedures.
- You are experiencing symptoms of peripheral artery disease (PAD), such as leg pain, numbness, or difficulty walking, due to poor blood flow.
Benefits
Interventional cardiology is an essential field that offers advanced, minimally invasive solutions to a wide range of cardiovascular conditions. By providing less invasive treatment options, interventional cardiologists help patients recover faster and with fewer complications, while effectively treating life-threatening heart and vascular diseases. Interventional cardiology offers several advantages over traditional open-heart surgery:
- Minimally Invasive: Most interventional cardiology procedures are performed through small incisions, reducing recovery time, pain, and scarring compared to open surgery.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Many procedures allow patients to return home the same day or after a short hospital stay, leading to faster recovery and less disruption to daily life.
- Reduced Risk: These procedures typically have lower risks of complications like infection, bleeding, or adverse reactions compared to open-heart surgery.
- Effective Treatment for Complex Conditions: Interventional cardiologists are equipped to treat complex cardiovascular conditions, including those that may not be suitable for surgery, such as high-risk or elderly patients.
- Quick Symptom Relief: Procedures like angioplasty and stenting can provide immediate relief from symptoms such as chest pain or difficulty breathing, improving quality of life.