Peak Heart & Vascular
Multispecialty Cardiovascular Group located in Laveen, Surprise, Avondale, Phoenix, and Flagstaff, AZ
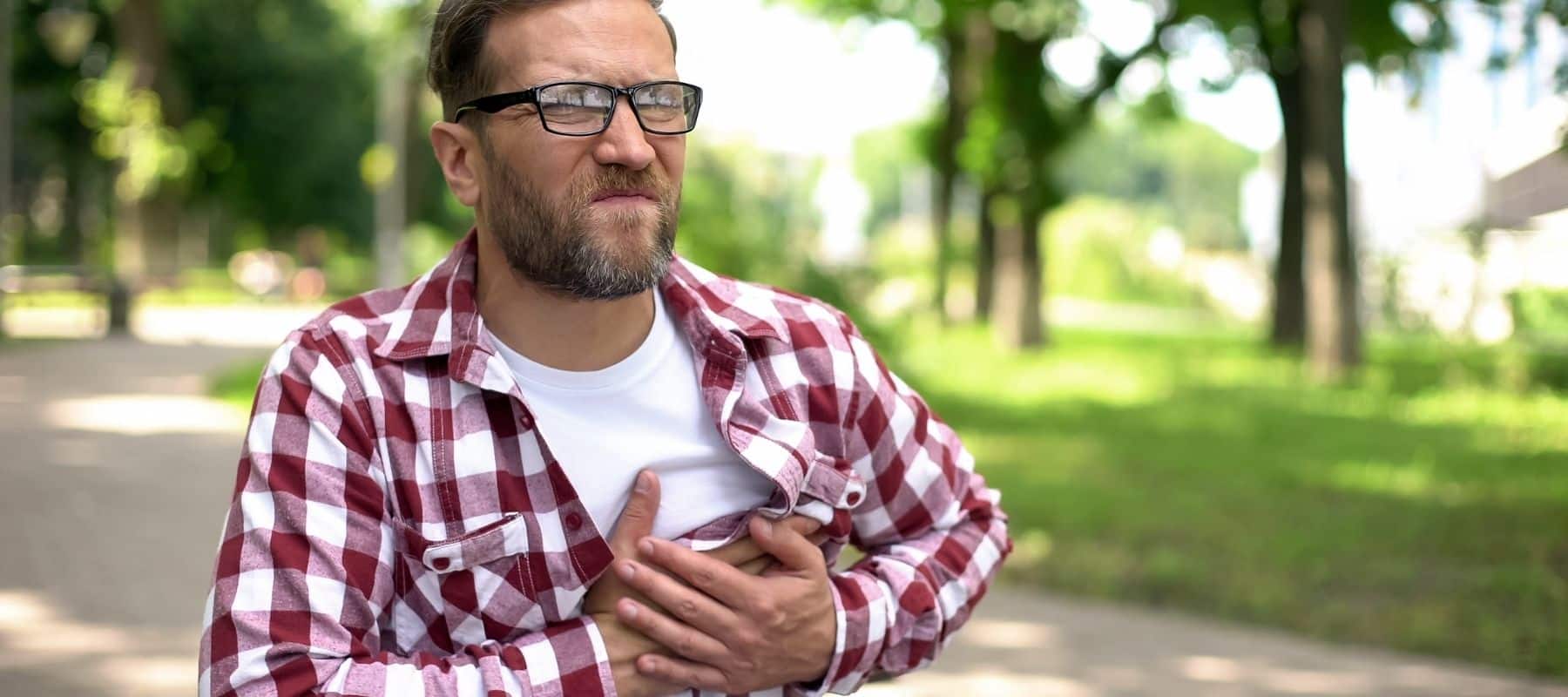
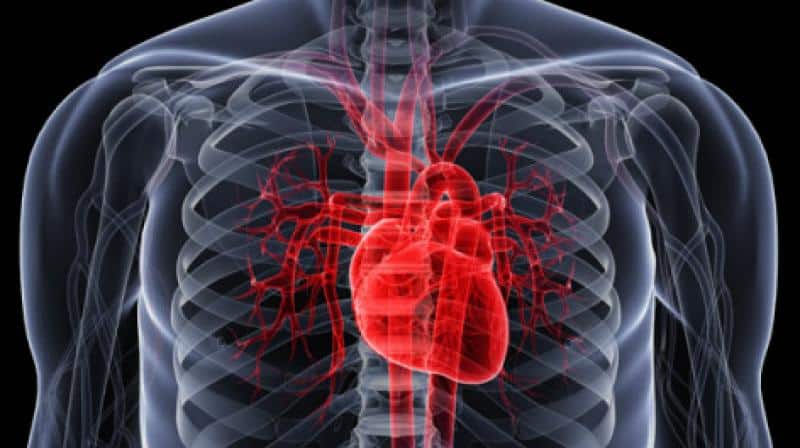
An abnormally fast heartbeat may be an indication that you have a condition known as supraventricular tachycardia or SVT. At Peak Heart & Vascular, the team offers comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services to identify the cause of your SVT. They offer a variety of services, including medication therapy and ablation procedures, to restore your heartbeat and prevent heart damage. Find out more about your options for treating supraventricular tachycardia today by calling the offices in Laveen, Surprise, Avondale, Flagstaff, and Phoenix, Arizona, or scheduling an appointment conveniently online.
Supraventricular Tachycardia Q & A
What is supraventricular tachycardia?
Supraventricular tachycardia is a condition that causes an abnormally fast heartbeat due to arrhythmias in the area above the ventricles. In a normal heart, the usual rate is 60-100 beats each minute. With supraventricular tachycardia, your heart rate exceeds 100 beats due to dysfunction in the electrical impulses that control your heartbeat.
What are the symptoms of supraventricular tachycardia?
For some with supraventricular tachycardia, there may be a few episodes of heart palpitations that come and go. In others, long-lasting symptoms can interfere with your usual routine. In addition to a rapid heartbeat, you can experience:
- Sweating
- Fainting
- Dizziness
- Heart fluttering
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
If persistent symptoms occur, it’s important to schedule an evaluation with the team at Peak Heart & Vascular for an accurate diagnosis.
What causes supraventricular tachycardia?
For some, an occasional rapid heartbeat may relate to stress or strenuous physical activity. Persistent rapid heartbeat and other symptoms may be due to:
- Smoking
- Heart failure
- Lung disease
- Thyroid disease
- Certain medications
You can also develop supraventricular tachycardia from drinking too much caffeine or alcohol or following surgery.
How is supraventricular tachycardia diagnosed?
The team reviews your medical history and discusses your symptoms during your consultation. To confirm a diagnosis of supraventricular tachycardia, they may order an electrocardiogram, which records the electrical activity of your heart.
A Holter monitor can also provide the team with a better overview of your heart’s activity over a period of 48 hours. You wear this device temporarily, and it doesn’t require any invasive procedures to gather data.
What treatments are available for supraventricular tachycardia?
If symptoms of supraventricular tachycardia persist, the team may recommend an ablation procedure to cure SVT or medications to control your heart rate and restore your normal rhythm.
Your provider may perform a catheter ablation. This procedure involves threading one or more catheters into the blood vessels of your heart. The catheters contain electrodes that damage small areas of heart tissue to address abnormal heart arrhythmias and cure SVT.
In some cases, you may need a pacemaker to control your heart rate. The team can determine whether you’re a good candidate for a pacemaker if other treatments aren’t working for you.
If you haven’t had a fast heartbeat evaluated, schedule a consultation today with Peak Heart & Vascular using the online booking feature or by calling the office.