Peak Heart & Vascular
Multispecialty Cardiovascular Group located in Laveen, Surprise, Avondale, Phoenix, and Flagstaff, AZ
Peak Heart & Vascular provides comprehensive cardiovascular care at various locations all over the Arizona area. Our providers offer services in General Cardiology, Preventive Cardiology, Interventional Cardiology, Heart Failure, Electrophysiology and Vascular Surgery. General Cardiologist focus on medical treatment for various heart ailments like blockages, heart attack, rhythm disturbances, high blood pressure, high cholesterol.
General Cardiology Q & A
When do I need to see a Cardiologist?
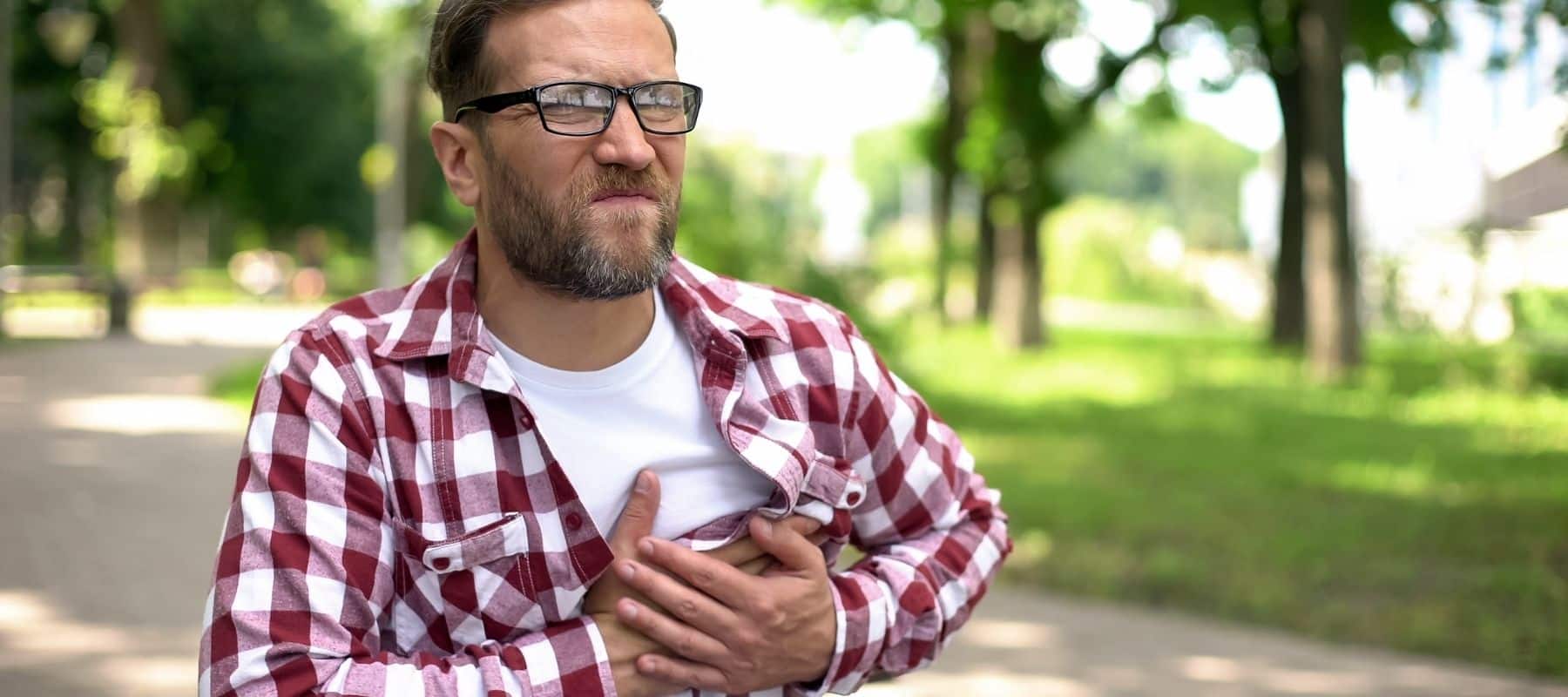
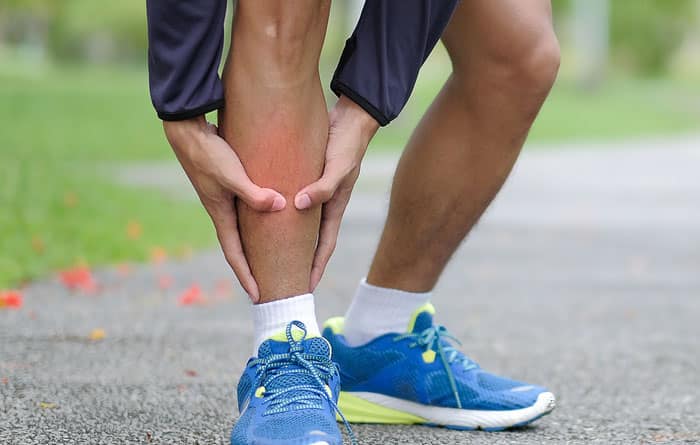
If you have any of the symptoms below, you should see a cardiologist right away.
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Palpitations
- Leg Swelling
- Fatigue
What are the common conditions treated by a Cardiologist?
- Coronary artery disease
- Hypertension
- High Cholesterol
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Arrhythmias
- Syncope
What to expect at first visit to the Cardiologist?
The cardiologist will complete medical history, physical examination and may order
some tests. Some of the tests which may be ordered include:
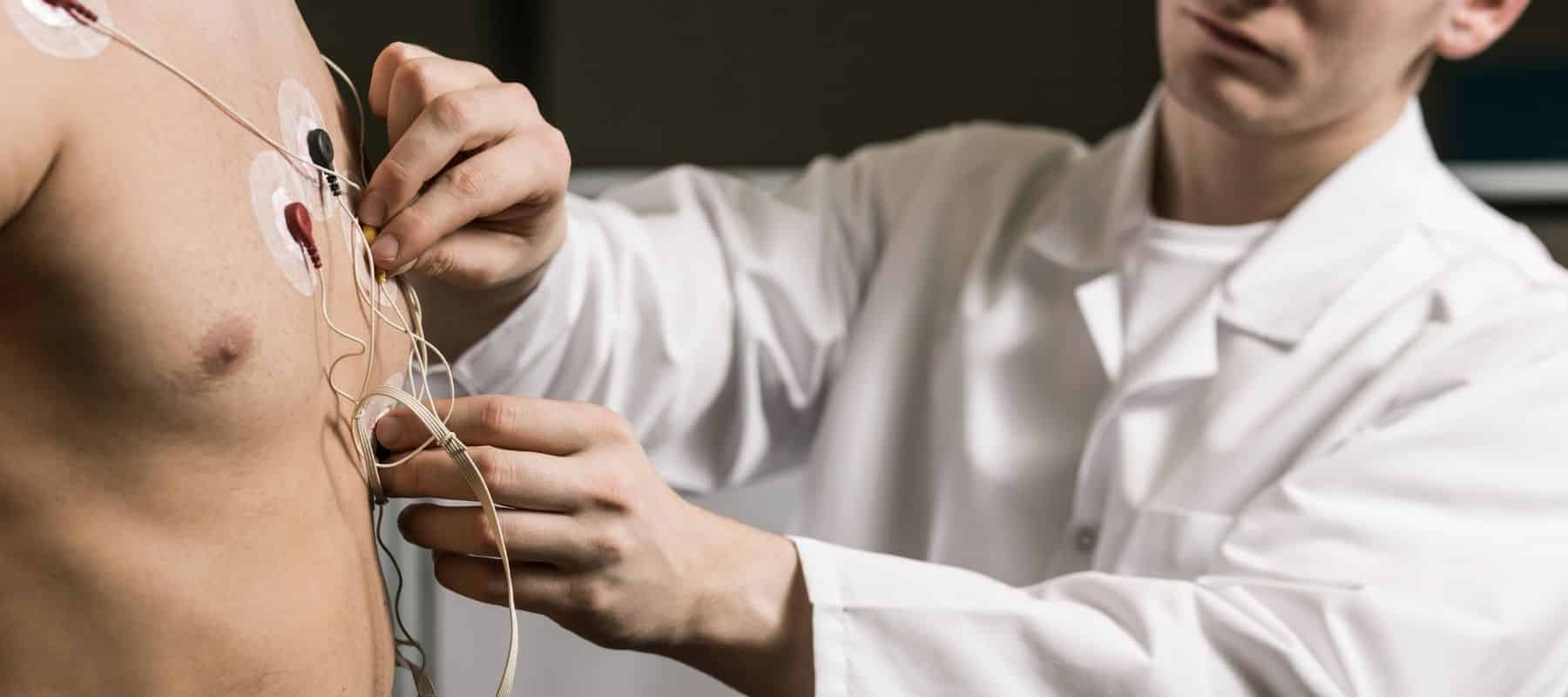
- Electrocardiogram
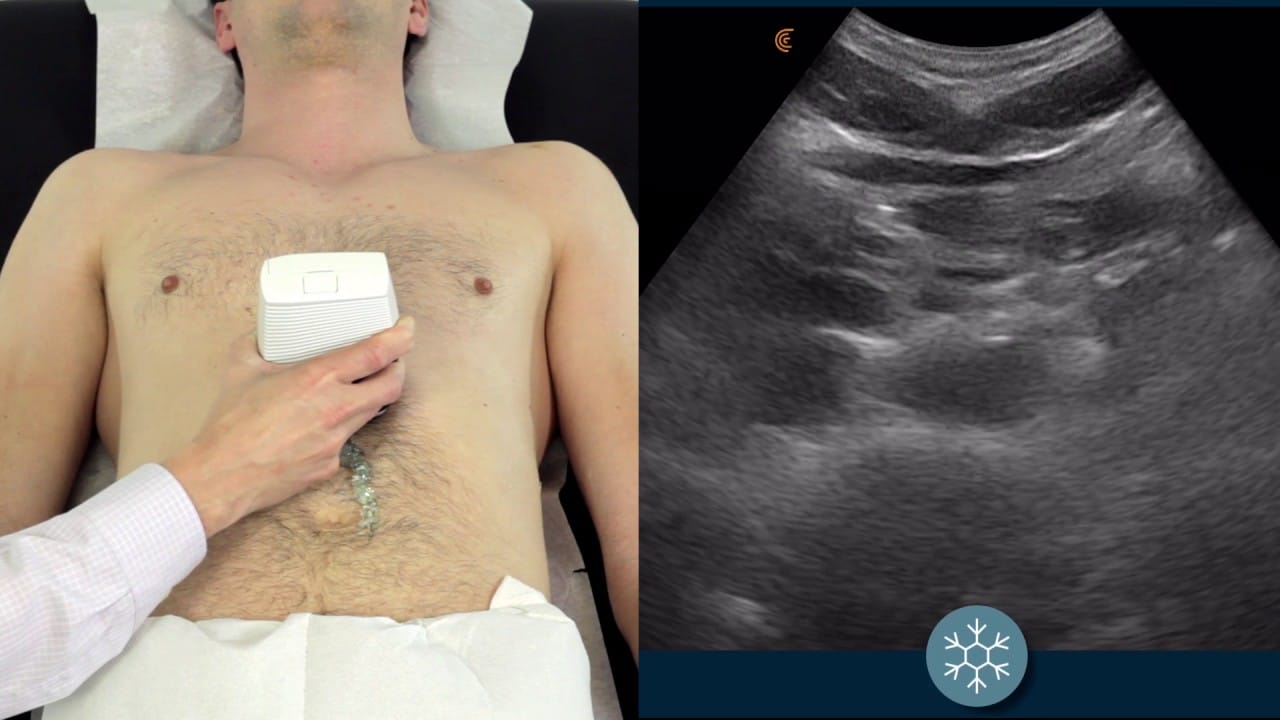
- Echocardiogram
- Treadmill stress test
- Nuclear stress test
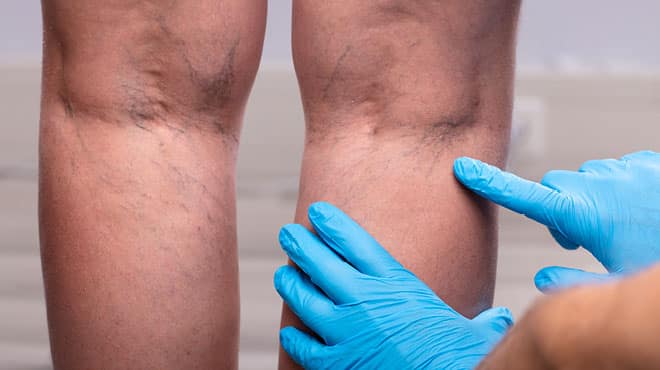
- Ultrasound of the legs
- Heart monitor